By: Paarvana Sree, Research Analyst, GSDN
Russia has been a trusted partner for India. Development of India-Russia relations have been a significant pillar of India’s foreign policy. By signing the Declaration on the India-Russia Strategic Partnership in October 2000, India-Russia bilateral ties have gained a new momentum with advanced levels of cooperation in almost all levels including security, defense, political, trade and economy, science and technology, culture and people to people ties. Further in December 2010 India and Russia’s strategic partnership was advanced to a high level of ‘ special and privileged strategic partnership’
Improving the trade and economic relation was the primary concern and considered as priority areas by both the nations. It is expected that bilateral investment will be improved by US$ 50 billion and that of bilateral trade to US$ 30 billion. According to the Department of commerce bilateral trade has reached US$ 65.70 billion in the 2023-24 financial year which is undoubtedly seen as a significant improvement.
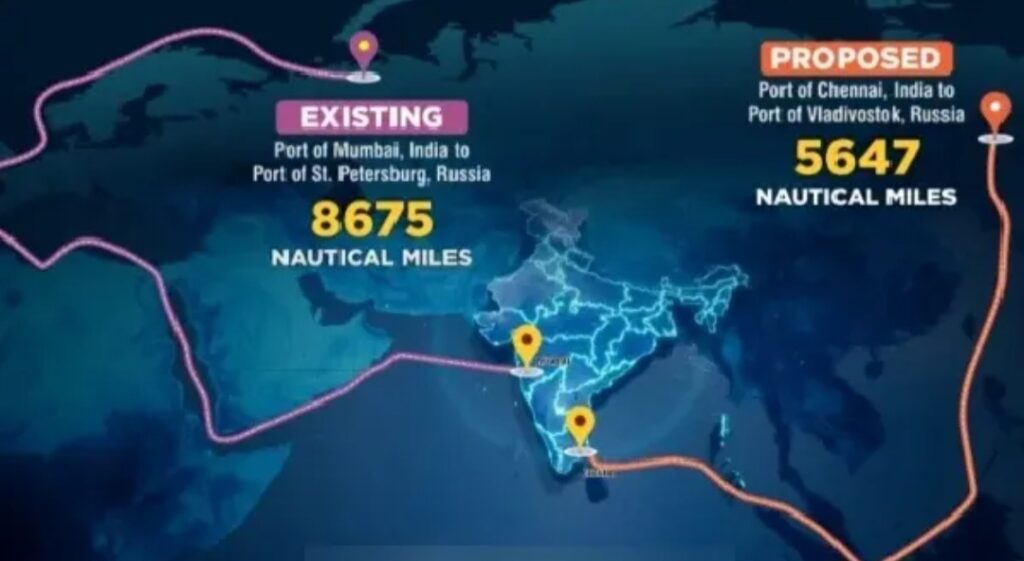
In 2019, Russia and India announced their desire to establish a maritime corridor between the ports of Chennai and Vladivostok. Both nations consider it as an economic and geopolitical project. The Chennai-Vladivostok link was operating for a few years during the Soviet Union period. And after years this link is put into consideration for its revival.
One of the primary reasons for India-Russia’s limited trade was the lack of connectivity. But now there is certainly an increase in the trade. The International North-South Transport Corridor (INSTC) which was established by Russia, Indian and Iran is operating only in specific parts. Both India and Russia remained politically trusted partners in terms of trade. However they faced a number of obstacles in carrying out their economic relations. In order to rectify this situation, the 2019 summit considered improving trade relations with special consideration given to the Russian Far East (RTE). The proposed Chennai-Vladivostok Maritime Corridor is significantly a part of this same vision.
Chennai – Vladivostok Maritime Corridor: A brief analysis
When Prime Minister Narendra Modi visited Vladivostok in 2019 to attend the Eastern Economic Forum (EEF) and annual Indo-Russian bilateral summit, a Memorandum of Intent (MoI) was signed by the officials on the’ Development of Maritime Communications between the ports of Chennai and Vladivostok. This maritime corridor is introduced to improve the bilateral trade between India and Russia. Presently India and Russia are connected through the Mumbai-St Petersburg shipping route. According to this, goods will take about 40 days to reach the destination. This proposed corridor sought to reduce the distance by saving economic costs. This corridor also has the potential to cover approximately 5,600 nautical miles which is about 10,300 km. As a result it will only take 24 days for the goods to reach the destination.
This corridor can be seen as an opportunity to India for realization of its ‘Act East Policy’. The Indian government can effectively manage its economic and political relations and also security concerns in the Indo Pacific region. This can be viewed as a ‘ game changer ‘ because it can add momentum to India and Russia’s economic relation. With the help of Russia, India is building a nuclear power plant in Kudankulam (Tamil Nadu coast). It is expected that this proposed corridor will automatically accelerate the project. This will also boost up India’s in land waterways with the aid of Russia’s low draft vessel technology system, which is one of the best in the world. Moscow’s increased participation in the project can assure the development of more than 5000 kilometers inland waterway and this can subsequently increase the cargo handling capacity by the ports for about 2,600 million tones.
Benefits for India
Both the countries Russia and India can attain numerous economic benefits by this corridor. It is known that the Middle Eastern region is the largest supplier of oil and Gas to India. This proposed corridor provides Indian companies and extraction opportunities in Russia’s Far East which will reduce India’s dependency on Arabian countries and subsequently provide energy security to India. Apart from this India will attain greater access to other resources like timber, forest resources, tin, gold, diamond, coal, nickel, rare earth minerals that the Russian Far East region holds. The Russian Government has already announced numerous initiatives to attract foreign investment in the region particularly in the areas of agriculture, infrastructure development, mining of mineral resources and precious metal deposits like gold, tin, tungsten and platinum. There are greater opportunities for collaboration in this aspect. India has announced US$ 1 billion ‘ Line of Credit ‘for the development of this region. Hopefully both the Indian and Russian governments will increase that trade relations to US$ 30 billion by 2025, through this sea route. This serves as a Geo political thrust to India and Russia’s strategic and mutual partnership in Indo – Pacific region in order to counter the Chinese dominance.
India’s geopolitical implications
No doubt that the Chinese government is a bit sceptical about the Chennai-Vladivostok corridor as it passes through the South China Sea. India has enjoyed an important position in the Indian Ocean. But presently it has been challenged by Chinese dominance. So this project is of great importance to India in order to regain its influence in the Indian Ocean as well as around its neighborhood. This trade route enables India to build its own trade route independent of China’s influence. It is also to be noted that India’s maritime presence will be notable by passing the Chennai-Vladivostok sea route from South China and building the essential potential for ‘ Indian Naval Operations ‘ in the Indo-Pacific. Thus, India can counter-balance China’s influence in the Indo-Pacific region by this corridor. Further India is initiating a strategic dialogue with US, Japan and Australia through Quadrilateral Security Dialogue (QUAD) in order to counter China’s influence in the Indian Ocean region.
Conclusion
For more than 75 years, India and Russia’s bilateral relationship has remained strong and stable. This relationship is considered as one of the powerful relationships in the contemporary world with shared understanding and common commitment to the multipolar world. It is to be noted that there has been a steady increase in the bilateral trade in the past two years. Also discussions are conducting for increasing exports from India as well as Russia. Many connectivity initiatives are conducted which is considered as pivotal for the bilateral cooperation including the Chennai-Vladivostok maritime corridor. Further both nations agreed to improve the cooperation in development of the Russian Far East region.
The Chennai-Vladivostok maritime corridor is now considered as an important project considering the economic and geopolitical interest of both the nations. The successful operationalization of this corridor will benefit both India and Russia to increase in trade and develop a vital and non-volatile channel for movement of goods.


Technology us There is definately a lot to find out about this subject. I like all the points you made